Chemiluminescent and Photometric Analysis of Matrix Gla Protein from Patients with a Defect of Musculoskeletal System
DOI:
https://doi.org/10.54779/chl20230694Keywords:
ELISA, levels of calcium and phosphates, bone metabolism, matrix Gla proteins, vitamin KAbstract
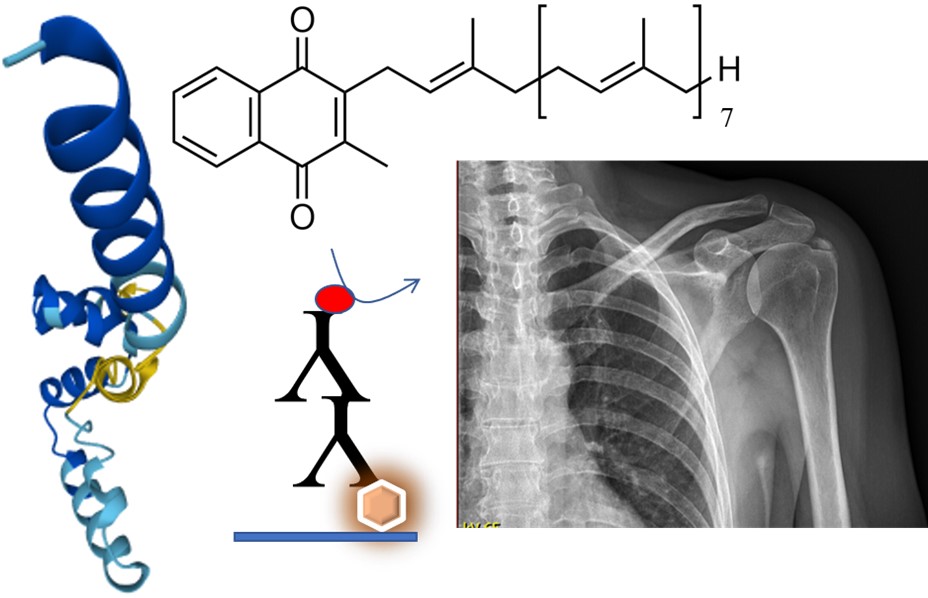
Matrix Gla protein (MGP) is a circulating protein with a low molecular weight that acts as a natural inhibitor of calcification. It belongs to the group of vitamin K‑dependent proteins. For its proper function, MGP must undergo vitamin K-dependent carboxylation and phosphorylation. Its main function is the prevention of soft-tissue calcification. It requires vitamin K2 as a cofactor for gamma glutamyl carboxylase. Vitamin K insufficiency is manifested by cardiovascular diseases, insufficient mineralization of bone tissue and the formation of calcifying deposits in soft tissues. The aim of this study was to design methods for monitoring the levels of MGP and dp-uc MGP by using immunochemical detection and to apply them to the analysis of real samples for use in clinical laboratories. These markers could serve as potential markers of the severity of joint diseases, cardiovascular diseases and also as markers indicating the status of vitamin K in organism.